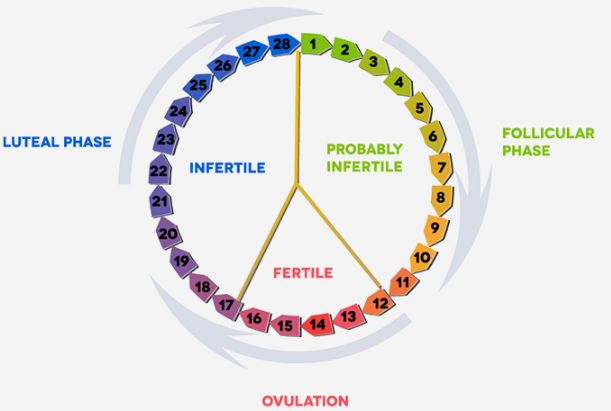
The luteal phase is something you should really consider understanding if you are trying to conceive.
The average length of a menstrual cycle is 28 days. However, it can vary from one cycle to another. It is also normal for women to experience cycles that last anywhere from 20 to 40 days.
Ovulation in most events is thought to occur in the mid-length of the menstrual cycle.
- Several factors such as stress, weight changes, and diet can greatly impact the luteal hormones.
- You should keenly chart down your cycle to get a better understanding of the events taking place in your reproductive system.
What is the luteal phase? (Meaning)

The luteal phase is the part of the menstrual cycle that begins immediately after ovulation. A woman’s menstrual cycle begins on the first day of the period and ends a day before the next period.
Majority of women have their menstrual cycle lasting between 21 and 35 days.
A typical luteal phase should last for about 12 to 16 days. During this period, the body prepares itself for pregnancy as the egg-containing follicle changes to a corpus luteum.
The Corpus luteum is responsible for the release of progesterone, a hormone essential for stimulating uterine wall thickening for implantation.
This phase is very important in a woman’s reproductive cycle if at all conception or pregnancy is to occur.
Early luteal phase
The early phase is marked by significant hormonal changes in the body. Several symptoms such as bloating and diarrhea signify significant hormonal changes.
The corpus luteum signals progesterone increase for thickening of the endometrium for possible implantation.
Mid Luteal phase

This is a period a week after ovulation has ended.
The progesterone levels are usually at the peak during this time. The endometrium thickens continuously as implantation usually takes place during this period. This is also the time that your doctor might want to carry out fertility tests because of the high progesterone levels.
Late luteal phase
This phase takes place few days before menstruation. After failed implantation, the hormones produced by the corpus luteum suppress production of follicle stimulating hormone.
Follicle stimulating hormone maintains the corpus. The corpus dies off as soon as the hormone levels subside.
The fall of progesterone levels triggers menstruation to take place and the beginning of the next cycle. Some of the late luteal phase symptoms include a thick white sticky discharge, bloating, nausea and abdominal cramps.
Luteal phase symptoms
Several events might lead to secretory phase insufficiency. The end of this phase is accompanied by a feeling of nausea, sweat, grumpy and depression.
These premenstrual symptoms are often as a result of the rise in progesterone levels. Lack of premenstrual symptoms signals low progesterone levels.

- Spotting happens when part of the endometrium lining breaks and bleeds even when you are not due for a period.
- Since progesterone keeps and maintains the endometrium, mid length bleeding could be a sign of a defect. Hormonal insufficiency often leads to miscarriages.
Fertility problems/problem conceiving could be a result of under-thickened endometrium. If an endometrium cannot be maintained, it will not support pregnancy after implantation.
Luteal phase defect (LPD)
A woman’s reproductive system is majorly controlled by two hormones. Hormone estrogen and progesterone rise and fall over the course of the menstrual cycle.
Progesterone is secreted by corpus luteum in the secretory phase and it remains high in levels in this phase because it initiates womb lining development.
- In cases where the corpus luteum fails to produce enough progesterone, the menstrual cycle might be thrown out of balance. This and more incidences are collectively termed as luteal phase defects.
- Symptoms of defects include spotting, miscarriages and the inability to conceive.
Causes of defects
The reproductive hormones are regulated by another set of hormones secreted by the pituitary gland. Follicle stimulating and luteinizing hormones are mainly secreted by the pituitary to oversee the functioning of the reproductive system.

If levels of these two hormones are altered, it could have major effects on the levels of progesterone and estrogen.
Here are the commonly known causes of luteal insufficiency:
1. Irresponsive endometrium
A luteal stage defect could arise when the endometrium doesn’t respond appropriately to progesterone.
The endometrium fails to thicken due to its insensitivity to progesterone. Pregnancy will not be a success in such a case.
2. Underlying health conditions
There is a range of reproductive conditions such as ovarian insufficiency, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and hypoglycemia that could lead to hormonal imbalances.
The hormonal imbalances are to blame for the unusual progesterone levels.
3. Progesterone insufficiency
Progesterone is produced throughout the menstrual cycle. Its levels rise immediately after ovulation has taken place.
If progesterone levels are not high enough after ovulation or if they drop too soon before menstruation, a short luteal phase occurs. Here are some of the common abnormalities related to progesterone.
4. Poor follicle production
If the pituitary gland fails to produce enough follicle-stimulating hormone between your last period and ovulation, the follicle becomes weak.
A weak follicle causes a thin uterine lining and an early period. These factors may inhibit fertilization and implantation from occurring.
5. Sudden drop in progesterone levels
If progesterone drops too soon after ovulation, then the body will automatically prepare for the shedding of the uterine lining. This is common with short cycles of 21-24 days.
6. Uterine lining failure
A fertilized egg needs a nourishing environment for growth and development. If the uterine wall is not thick or strong enough, it can only sustain this embryo for a few days and a miscarriage will occur.
Estrogen also thickens the uterine wall and in some cases, it fails to increase due to a decrease in progesterone levels.
Prevention of defects
Defects of the luteal stage can be prevented by practicing the following:
Stress reduction
Cortisol is a hormone produced during stress. It is produced first then your reproductive hormones. This means that in a stress episode your body throws progesterone and estrogen on the back burner.
Stress hinders conception in many different ways. Always keep your stress hormone under control by practicing good self-care habits such as exercising.
Get enough sleep
The reproductive hormones are influenced by your sleeping patterns. Getting enough sleep each day not only helps you reduce stress but also improves your overall reproductive health.
Healthy eating habits
Eating too much can cause obesity while eating too little leads to anorexia. You are advised to eat acceptable amounts of food to help prevent negative impact on your hormones.
To cure a luteal insufficiency, you need good amounts of nutritious foods while cutting down on sugary foods such as cakes and soda.
Luteal phase length
The length of this phase is important for the survival of early pregnancy. The phase length is determined by counting the number of days that are between the last day of ovulation and the day just before your period.
- How long is the luteal stage on average? A normal phase is usually 12-16 days and 14 is the average length. However, some women have a short phase of fewer than 10 days.
- You can measure your luteal length by use of hormonal kits or simply watch for signs of ovulation and chart until a day before your period.
9 day
A 9-day luteal length is short and could make it impossible for an egg to implant. By the 9th day, the uterine wall will be breaking down in preparation for a period.
It is advisable to visit a doctor and learn how you can lengthen your secretory phase for a successful pregnancy.
10 day
Women with a 10-day luteal length might experience difficulties getting pregnant because this period is not enough for production of progesterone which is responsible for the thickening of the endometrium. Continued use of treatments to lengthen the phase might lead to a successful pregnancy.
11 day
An 11-day luteal length might allow implantation to take place. However, chances of the embryo survival are less because this phase length will not allow proper thickening of the endometrium to take place.
You might need to talk to your doctor about the use of natural treatments and other available supplements before conception and during the first and second trimesters of pregnancy.
12-day phase
A 12-day long luteal length is considered problematic too when it comes to conceiving. The uterus needs at least 14 days to build its lining and prepare to carry a pregnancy.
If the corpus luteum dies 12 days after conception, there may not be sufficient progesterone to sustain a pregnancy. A miscarriage is likely to occur.
16-day phase
My luteal phase is 16 days, could I be pregnant? Yes and no. An average phase is usually 14 days. For a 16-day phase, you might want to take a pregnancy test.
Apart from pregnancy, an underlying medical condition might be a cause of a long luteal stage. You are advised to test for pregnancy and if negative, visit your doctor for further test and investigations.
Short luteal phase
Short LP (Image source: Fertility Friend)
The phase length is significant in the woman reproductive cycle. Unfortunately, some women have short phases. This can be termed as a luteal phase defect. A short phase is one that lasts less than 10 days.
In case pregnancy occurs immediately after fertilization, a miscarriage is likely to occur because of a short luteal stage. The uterine lining must be thick enough for proper attachment of the embryo.
Can you get pregnant with a short luteal phase? A short phase makes it difficult for pregnancy to occur since the body fails to secrete enough progesterone responsible for uterine lining thickening.
However, this is not a reason to be so alarmed. Once the hormones go back to normal, you can have a good chance to conceive and have a healthy baby afterward. Talk to your doctor about how you can get your phase into shape.
Symptoms
It is unlikely that you will notice any defects with your secretory phase unless you are unable to conceive. The following are signs to signal you of a short luteal phase:
- Earlier than normal menstrual cycle
- Spotting between your periods
- Miscarriages
- Inability to conceive
Causes of a short luteal phase
Hormonal problems and poor nutrition are the main causes of a short LP. It is believed that fixing these problems will also encourage a normal length of this phase. This will also lead to improved fertility.
- Lack of proper nutrition
The primary cause of short luteal phase is lack of proper nutrition. This means that your body may be lacking certain vitamins, minerals and other essential nutrients that help support proper functioning of the reproductive system. The corpus luteum controls the length of the secretory phase.
- When the corpus luteum lacks proper nutrition to sustain itself, it degenerates prematurely (usually less than nine days) leading to a luteal insufficiency.
- Hormonal imbalance
There are several factors attributed to hormonal imbalance. The most common include improper nutrition, presence of toxins in the body and lack of exercise. Estrogen dominance as a result of overweight is the main reason for infertility in women. Other causes include
- Aging
- Excessive exercise
- Anorexia
- Thyroid gland disorders
- Obesity
- Stress
- Endometriosis
How to lengthen a short luteal phase
Normally, a disruption in the secretory phase can be a cause of alarm. Not only does this affect your whole menstrual cycle but also your fertility.
- A secretory phase of fewer than ten days does not give the uterus adequate time to establish a thick lining for the embryo thus a miscarriage in case of fertilization.
Diet is the foundation of hormonal health. Supplements also work well when it comes to solving defects associated with a short cycle. Additionally, changing your overall lifestyle is a better way to enhance a long luteal stage. Here is what to try to lengthen a short secretory phase
1. Diet
Vitamin C: Studies have shown that vitamin C significantly increases levels of progesterone.
Examples of these foods include bell peppers, broccoli, Brussels sprout, papaya, strawberries and citrus fruits. A daily recommended dosage of vitamin C is 750mg.
You can choose to obtain vitamin C from fresh vegetables and fruits or simply take a supplement with the same value.
Green vegetables: Green vegetables are rich in vitamin B complex.
It is essential for hormone regulation. They are also high in magnesium and calcium which inhibits premenstrual symptoms associated with low progesterone levels. The daily recommended value of green vegetables is a 2-5 cup of cooked vegetable. There are a variety of these veggies including kale, collard greens and spinach.
Essential fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for development of the endometrial lining for implantation in case you are trying to conceive. Sources include salmon, halibut, sardines, walnuts and chia seeds.
Proper cholesterol
Steroidal hormones including progesterone are synthesized from pregnenolone. It is derived from cholesterol.
Adequate consumption of dairy is important for the nourishment of the uterus. Other sources include eggs, grass fed butter and animal protein.
2. Supplements
Saffron
Saffron is commonly used as a spice in the kitchen. It is essential in curbing symptoms of low progesterone including dysmenorrhea. Take 15mg of this natural treatment daily for better results
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B complex has been found to have a major effect on overall health while vitamin B6 works great in the luteal stage.
It is always advisable to take the two vitamins concurrently for better results. The recommended daily dose of vitamin B6 is 60-120mg.
Excess intake of this vitamin causes nerve toxicity. It is therefore important that you do not take more than the recommended dosage.
Vitex
This is one of the most used natural treatments vital for lengthening a shorter secretory phase. It is essential when it comes to regulating and restoring progesterone levels.
It is available in capsule or tinctures. The daily recommended dosage is 1000 mg.
3. Important practices
- Charting your period: Always use the fertility awareness method to chart your fertility. This method will show you how long your phase is and will help you determine any defect or abnormality.
- Acupuncture: This practice has shown to smoothen out hormonal imbalances.
Weekly acupunctures will help increase your fertility rate and regulate your menstrual cycle. Try acupuncture sessions weekly for at least three months to determine its effectiveness.
Long luteal phase
It might be confusing when you get a late period and a negative pregnancy result.
A long phase means that the body continues to produce high levels of progesterone for more than 16 days past ovulation. Here are two common causes of a long luteal phase
- Pregnancy
If your secretory phase is longer than 16 days, you may want to take a pregnancy test. A negative pregnancy test after 16 days should prompt you to ask your doctor to take blood tests since the pregnancy hormone might take a little longer to test in urine.
- Underlying medical condition
Certain medical conditions such as Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome can cause serious hormonal imbalances. Sometimes progesterone stays elevated even after 16 days past ovulation. You may want to visit your doctor for tests and examinations.
How to deal with long luteal phase
A short luteal phase might give you sleepless nights if you are trying to conceive because the fertilized egg has fewer chances of implantation.
The only way you can track your phase length is by keeping accurate records of your basal body temperature.
- A secretory phase with elevated BBT 3 days longer than your last cycle could be a sign of pregnancy.
- See your doctor to clear up the confusion if at all you do not have a positive pregnancy test.
How to calculate your luteal phase
It is important that every woman understands the length of their luteal stage to be able to plan for conception properly.
As earlier said this phase begins immediately after ovulation and continues until the next day before your period. It is not easy to calculate your phase length without knowing ovulation.
To know when you ovulate you need to keep charting your temperature every day of the month. An increase of about 0.5 degree signals ovulation.
Also look out for other signs such as breast tenderness and increased cervical mucus. To calculate your luteal phase you need to count the number of days between the last day of ovulation up to a day before the start of your period.
- A normal secretory phase is usually 10-16 days. You should always chart daily temperatures and symptoms to help you determine which days your ovulation is occurring.
Treatment and natural remedies
Experiencing luteal insufficiency when trying to get pregnant is quite distressful. However, there are treatments available for the condition across different stages of your menstrual cycle.
Other than prescribed medications, natural treatments also play a greater role in inhibiting luteal insufficiency.
Below are treatments and natural remedies effective for correcting defects associated with this phase:
1. Clomiphene
In this kind of treatment, ovulation is induced as soon as the menstrual period starts. The most common prescribed medications are clomiphene (Clomid) and Gonadotrophin for inducing ovulation.
The most common side effects of these drugs are multiple births. Clomid also stimulates the growth of follicles to increase your chances of producing a higher quality egg. You need to talk to your doctor about other risks and benefits of such treatments.
2. Progesterone supplements
After ovulation, the endometrium begins to grow in anticipation for implantation. Progesterone supplements might be prescribed to help support the thickening of the uterine wall.
Another hormone known as Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (HGCH) may also be injected in the luteal phase to help stimulate the corpus luteum into releasing more progesterone.
3. Vitex (Agnus Castus)
This is one of the most used natural treatments to get rid of luteal phase defects. Vitex is a whole food supplement made out of berries of a Castus plant.
Vitex is a known hormonal imbalance remedy. It works to regulate the menstrual cycle and also lengthen a short luteal stage.
Studies have shown that vitex helps regulate progesterone levels and increase the secretory phase to enable implantation to take place.
- Vitex is safe during pregnancy.
- It can also be taken daily for a month when one is trying to conceive.
This natural treatment might take a while before you can notice result. It is therefore advisable that you remain patient.
You are likely to notice changes after 3 months after the remedy has built its effects in the body. Vitex is recommended until 10 weeks for the support of the corpus luteum growth.
4. Red raspberry tea
The raspberry leaf balances hormones and also nourishes the uterus. It is one of the most excellent natural treatments when it comes to luteal insufficiency. Raspberry is best when taken as infusion tea. It is excellent in balancing the whole hormonal system.
How to prepare:
- Take a glass of dried raspberry leaves and put into a glass jar
- Pour 6 glasses of boiled water over it and put a lid on it to sit overnight
- Strain and refrigerate
- Drink at least 3 glasses each day
- You can mix with mint leaves for a better taste
You can continue drinking a cup daily after conceiving, two cups in the second trimester and three cups in the third trimester. The raspberry also tones the uterus in readiness for labor and delivery.
Vitex with raspberry works much better when infused together. The two are known to highly enhance fertility.
5. Fertility Cleanse
Of the natural treatments, herbal cleanse is one of the most effective in getting rid of body toxins. The cleanse helps regulate the hormones by shedding off excess levels .This lengthens your secretory phase.
The fertility cleanse sets your body and prepares it for pregnancy. The fertility cleanse kits are available at pharmaceutical outlets but its good always to inform your doctor before purchasing one as he may suggest the most effective of them all.
6. Progesterone Cream
One cause of luteal phase defect is low progesterone levels. A good quality of natural treatments of progesterone can help sustain the corpus luteum and extend the secretory phase for implantation to take place.
Progesterone creams are best used during the secretory phase and not all along the cycle. In this phase, progesterone is supposed to be higher than in the follicular phase. If the progesterone cream is used before ovulation occurs then you might just prevent ovulation from taking place.
You can also continue using progesterone cream even after confirmation of pregnancy to prevent miscarriage due to a sudden drop in levels of progesterone.
Wean progesterone off slowly from the 10th week of pregnancy. Always discuss with your healthcare provider for your use of progesterone cream.
SOURCES AND REFERENCES
- Menstrual cycle (May 2013): https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/normal-menstruation
- Female infertility (June 2016): http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/female-infertility/symptoms-causes/dxc-20214762
- The other time of the month (August 2016): http://www.webmd.com/women/features/other-time-of-month#1