It is not healthy when your dog scratching or licking itself all the time. Chances are that it is due to an infection or infestation of some kind.
When you see scabs on the dog, it means that the animal needs to be taken to the vet for treatment. If your dog has crusts on its skin, the following sections will detail out all you need to know.
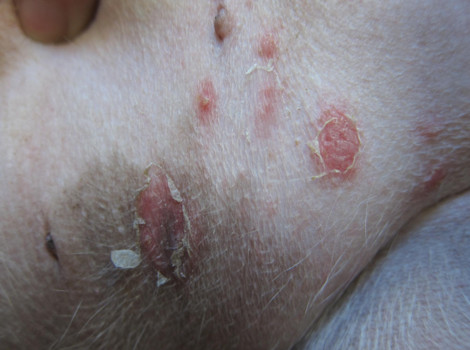
What are scabs?
Scabs occur as dry and protective crusts on the wound when it is about to heal. These scabs may not have an obvious cause since many different conditions can cause them.

The scabs may also differ in their characteristics such as being dry, crusty, brown, white, black and so on. They may also occur on the legs, the belly, neck, head, ears, skin, back and many other places on the body.
Causes of crusty scabs on dogs
There is a long list of the reasons behind the scabs on your dog. The range from allergic, hereditary, parasitic, environmental and many others in nature. Depending on the causes, the scabs will have different traits with some appearing in specific place while others covering the whole body.
Among the causes of the black crusts are the following:
1. Allergies
There are many allergies among dogs whose symptoms include irritation of the skin. The skin is most inflamed and irritated when the dog has contact allergies. Ingesting allergens will cause a reaction on the skin which will end up forming crusty patches.
At times, the scabs are a direct result of an allergic reaction in the dog. They start off as itchy bumps on the skin which, after scratching from the dog, turn to crusts.
To resolve this issue, you need to know exactly what is causing the skin allergic reaction.
Among the most common allergies in dogs are:
- Food allergies
- Contact allergies
- Airborne allergies
- Flea allergies
Any of these can lead to scabs.
2. Parasites
Parasites such as chiggers, gnats, mites, fleas, lice and insects often bite the dogs leading to licking and scratching which damages the skin. When the wounds start healing, they will likely form scabs on the skin.
The same parasites lay eggs on the dog’s skin irritating it in the process. The dog will start biting, licking and scratching its skin with the result that sores and bleeding will occur. As the itching persists, the scabs will become bigger with time.
3. Poor nutrition
Even in humans, the skin is the fast sign of the health of the individual. In dogs, any deficiencies in the nutrients will lead to a poor coat which easily develops problems.
When the body lacks the minerals and vitamins, it will be hard to defend against parasites that will attack the skin and cause crusts. The same will occur if the immunity of the dog goes down and opportunistic diseases take over.
4. Too much grooming
You should clean your dog as often as reasonably possible. If you do it too often, you will damage his or her skin and cause scabbing and even ingrown hair on the skin.
Too much cleaning will do away with the natural oils of the skin leading to a dry skin that develops scabs. Due to the lack of oils, the skin will start flaking and itching hence scabbing.
Using the wrong skin products such as harsh shampoos also have the same effect on the skin of your dog. The use of mild shampoos and keeping the cleaning to about once a week will ensure your dog has a healthy coat free of blemishes.
Types of crusts and where they can be found
Scabs can be of different colors, shapes and general feel. They can also be found on various parts of the body including the back, the ears, neck, tail, snout and other parts.
On the back, snout and tail
When you see your dog with a crusty dry nose or snout with flaking and scabbing, it could be a sign of sunburn. This type of scabbing is hard to notice but is often quite harmful to the dog and needs to be addressed as soon as possible.
If the crusts are on the tail or back of the dog, bacterial infection is the likely cause of the scabbing. Infections such as folliculitis often cause welts and sores on the dog’s skin. The sores and welts may be accompanied by blisters filled with fluid on the belly, back, tail and elbows. If they occur in puppies as often is the case, it would be due to impetigo.
On the neck and head
If you see scabs on the neck and head of your dog, chances are high that it is caused by a bacterial infection called pyoderma.
This kind of infection occurs secondary to allergies. Getting rid of this condition requires the use of oral antibiotics and medicated shampoo.
The dry patches will often manifest as pus-filled bumps on the head and the neck. As the bumps build up, they turn to crusty scabs.
Due to the close relationship these scabs have with allergies, treating them requires the use of hypoallergenic diets. These control the allergic reactions in your dog. The vet should still be consulted on the matter.
On the legs and belly
Bacterial infections often lead to scabs that are smaller in size than other scabs especially on the legs and belly of the dog.

These scabs are most likely to appear during the warm weather conditions such as the summer when the symptoms of the infections are at their peak.
The dog’s skin has staph bacteria although in controlled amounts. When the bacteria overgrow, it will lead to scabs on the belly.
On the ears
While scabs on the ears are not as common as on the other parts of the dog, when they occur, it is often a case that needs the attention of the doctor.
It could be an infection whose symptoms are the scans on the ears. It could also be a flea infestation which requires proper treatment.
At times, it could be due to sarcoptic mange. The cause of sarcoptic mange is microscopic mites which cause the dog to itch and scratch itself a lot. At times, the dog may develop an allergic response to the mites thus worsening the condition.
Given the mites’ preference for areas without hair on the body, you are likely to see black scabs on the elbows, belly and ear flaps of the dog. The mites may also make the skin scaly and red. For such cases, only the correct diagnosis of the doctor will save your pet.
Sarcoptic mange can spread from one pet to the next through contact. Thus, if your dog has it, it can pass it to the other dogs and even to the cat and other furry pets in your home.
On the back
Scabs on the back is a common phenomenon in dogs. The back is exposed to the environment and will thus be among the first places the signs of an infection will appear. They could be caused by many different reasons among them the ones stated above.
Depending on what caused them, the scabs on the back of your dogs can be of a white or black color. If the scabs form after the dog had been scratching itself, fleas are among the first suspects.
If this is the case, then you are not bathing your dog as frequently as needed, or you are not doing it right. After the bath, give your dog the needed tropical treatment to kill any remaining fleas.
At times, the flea infestation might be so intense that the dog will shed some hair off its skin. Such cases require the attention of the vet as soon as possible.
Treating the crusty scabs
Once scabs have been noticed on the skin of the dog, you need to act fast to prevent their progression to worse skin conditions. Treating the scabs on your dog will start with the identification of what is causing the scabs in the first place.
Start by referencing the scabs to the symptoms to know what is causing them. You can do so by first identifying the characteristics of the scabs such as their color, dryness, crustiness and so on.
If you find out that cause of the scabs can be dealt with at home, start by carefully trimming the hair around the scabs to allow for ease of monitoring and treatment. Trimming the hair also improves aeration to it making it dry hard for the bacteria to propagate further.
Clean the area (or the dog itself in full) after finding the scabs. This reduces itching and thus the first step towards stopping the scabbing.
For cleaning, use hypoallergenic shampoo that is mild to prevent further damage to the skin. If the area is swollen, use a cold compress on it. If, on the other hand, the area makes the dog bite and lick itself, the use of E collar is recommended.
Any medicine from the pharmacy should be used strictly according to the instructions given.