How common is Zika virus during pregnancy? Does it cause birth defects and side effects on future pregnancy? Is there a vaccine for this virus? Here are facts you need to know about this virus.
About 80 percent of people infected with zika virus will not become ill. However, the 20 percent present with symptoms similar to those of a mild flu. Studies have shown that pregnant women are likely to be at greater risk, because of their obvious reduce immunity.

- The facts remain zika virus causes birth defects over a large number of populations.
- It is therefore important that a woman takes up all precaution measures before conception, during pregnancy, and after childbirth.
- This is to ensure that her health and that of her baby are not compromised.
The center for Disease Control (CDC) suggests that all women living in zika-affected areas should get tested as part of their prenatal care. Testing for the virus should continue through second trimester and the baby properly examined after birth.
What is Zika Virus?
Zika Virus a vector-borne disease transmitted by Aedes mosquito, the same one that transmits dengue and yellow fever. The zika name originates from Uganda, where the virus was first detected in 1947.Zika virus is related to yellow fever, dengue, and Japanese encephalitis. The virus has spread from its origin in the narrow equatorial Africa to Asia over the years.
- There have been zika virus epidemics in other parts of the world raising major health concerns.
- Guidelines are issued to ensure the whole population especially pregnant women remain unaffected.
Symptoms of Zika during Pregnancy
Signs and symptoms of zika virus usually begin from the 2-7 day after exposure to the virus. You can be ill for several weeks as a result. Here are symptoms to look out for:
- Severe frontal or a general headache
- Joint or muscle pain
- General body rash
- Nausea and vomiting
- Conjunctivitis(Pink eye)
- Fever
Signs and symptoms of zika can be relieved by:
- Getting enough rest
- Drinking plenty of fluids
- Taking pain relievers
- Taking antipyretics (drugs to relieve fevers)
Zika virus and pregnancy
Can Zika affect my pregnancy? If a woman is infected with zika, there is a chance the virus will pass to the unborn baby and cause defects.
In case that happens, your baby will be at greater risk of developing conditions such as microcephaly and brain damage. It may also cause the baby to suffer from eye problems, hearing defects and movement related conditions.
Additionally, zika virus can also lead to still births and miscarriages. In other cases, a baby might be born normal, but later on develop slowed head and brain growth.Zika is considered dangerous at any stage of pregnancy
How does zika virus spread?
Zika spreads through different ways. Here are the known ones:
1. Through mosquito bites
This is the most common way zika spreads. You can get infected by a mosquito carrying zika virus. Consequently, a mosquito can get the virus by biting an infected person.
Since zika virus can stay in the human body for some days or weeks, the mosquito can pass the virus until the 12th day after biting an infected person. The zika virus mosquitos usually bite during the day, and the mosquito can live both inside and outside.
2. Mother to baby through pregnancy
The virus can pass through the placenta to the baby during the baby’s growth and development period in the womb. The virus has been tested in the amniotic fluid, and this is evidence that the virus can go through the placenta barrier and cause defects to the growing fetus.
3. Through body fluids
Body fluids such as blood, semen, and saliva highly transmit the virus. Blood should be thoroughly screened before transfusion is done. The virus is highly present in blood than in other body fluids
4. Through sex with an infected person
During sex, an infected male can pass zika virus through the semen. The virus stays in the male semen for at least two weeks and more than 4 months after signs and symptoms begin to show. Similarly, an infected woman can pass the virus to her partner through vaginal fluids. The virus can last up 12 days after her signs and symptoms begin.
Baby Birth defects with Zika Virus

Recognizing that zika is a cause of particular birth defects does not mean that all pregnant women infected with zika will not have normal babies. It simply means that this infection during pregnancy increases the chance of these conditions.
Research is ongoing on how zika affects pregnant mothers and their children to help better understand the severity of this virus. Below are 3 common defects as a result of zika virus infection:
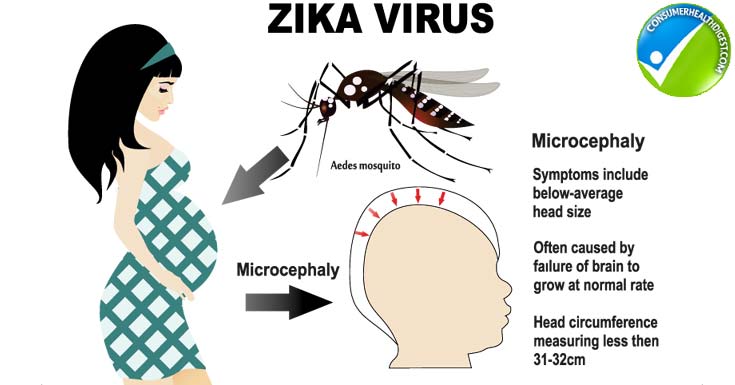
1. Microcephaly
Microcephaly is a condition whereby the baby’s head is smaller than the expected, when compared to other babies of the same age and sex. This condition affects the brain, and in that case, it does not grow properly as expected.
Microcephaly can occur because the baby’s head has not developed properly during pregnancy or even after birth.
2. Congenital zika syndrome
Congenital zika syndrome is another widespread birth defect as a result of the virus. This syndrome is described using five major features:
- Severe microcephaly where the skull has partially collapsed.
- Decreased brain tissue with particular pattern and brain damage
- Pigment changes or damage to the back of the eye
- Limited joint movement.
- Too much muscle tone causing movement restriction soon after birth.
Most babies infected with zika syndrome have been associated with significant eye problems. In case your baby is born with eye problems, quickly should ask for recommended tests and screenings to test your baby to check for eye and other underlying problems.
3. Gullaine Barre syndrome
This is a condition whereby the immune system attacks the peripheral nerves. It simply affects people of all ages. Severe cases of Guillain Barre Syndrome are rare, but when it occurs, it can lead to total paralysis. Treatments for this condition include supportive care and immunological therapies.
According to the World Health Organization” There is a significant rise in some cases of this syndrome in areas where zika virus has been reported.
Guillain-Barre is often preceded by an infection mostly bacterial or viral. Research claims that the zika virus triggers new cases of the condition or simply worsens the already known cases. The most common symptoms of Guillain-Barre include:
- The weakness of the muscles, usually starting from the legs spreading to the face.
- Inability to properly swallow and chew in severe cases
- Paralysis of the legs, arms or muscles of the face in some case
How long does zika stay in the body?
Dr.Denise Jameison, a member of the zika response team from CDC, claims that the virus stays in the human body for at least two weeks. `If zika virus stays in the body for more than two weeks , then you must be pregnant. Expectant mothers’ immune system is temporarily altered.”
- However the virus stays longer in the male semen, because of that, men should wait for at least six months before planning to get a child.
- Also, couples who travel to zika prone areas are advised to wait for at least six months before planning a pregnancy even if they have no symptoms of the related virus.
How long should I wait before I can get pregnant after being infected with zika?
To avoid the effect on future pregnancy, women who might have been exposed to the virus, through travel or sex should wait for about eight weeks before getting pregnant. However, men who have been exposed to the virus should wait for at least six months before trying to conceive a pregnancy.
It is advisable that one waits for the stipulated time, even if they don’t have the symptoms since the virus may take time to clear off the body.
During the wait time, both men and women are advised to use protection during sex and use effective birth control measures to avoid pregnancy. It is doubtful that one could get again after the first time.
Is there a test to tell if I have been infected with zika and when should I test?
Yes. There are various tests that are used to test for the virus. However, it all depends on how long you have had the symptoms or exposed to the virus. Here is when to test for the virus:
- Test after being exposed to the virus and have had symptoms any time or during pregnancy
- Carry out the tests when you live in or frequently travels into an area with risk of zika, but no symptoms
- You are also advised to test when you have had sex with an infected person without a condom
- You are also encouraged to test after being exposed and given birth to a baby whose birth defects are potentially associated with zika virus.
What if am pregnant and test for zika, or what happens when my results are not clear?
According to the guidelines provided by the CDC, here is what to expect as part of prenatal care:
1. Fetal Ultrasound
The fetal ultrasound is performed in pregnancy between 18-24 weeks. The main reason for an ultrasound will be to assess the general anatomy of the baby. Birth defects such as microcephaly and intracranial calcifications can be detected from 20 weeks of pregnancy.
The ultrasound also provides facts about the fetus neural developments and other brain structural abnormalities that might exist way before microcephaly.
Ultrasound has been used for so long in the clinical setup, and it has not been associated with adverse fetal or maternal effects.
However, the accuracy of the results depends on factors such as gestational age, equipment used and skills of the person performing the ultrasound.
A routine ultrasound is recommended because an absence of microcephaly on one time does not exclude future microcephaly or intracranial calcifications.
2. Fetal Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
The fetal MRI is used to answer facts about the fetal ultrasound. It is therefore not an everyday kind of a procedure, and it can only be used in high-risk situations.
3. Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure in which a small amount of fetal fluid is removed from the sac surrounding the fetus, for testing. The considerations for the procedure vary with the patient’s clinical circumstance.
- This procedure has been used for many years to evaluate other congenital abnormalities. It is reliable and accurate even though it is associated with some risks such as embolism. Amniocentesis is recommended until after 15 weeks of pregnancy.
- Experts claim that there are fewer risks associated with the procedure when it’s done above 15weeks of gestation.
The best time to carry out amniocentesis to diagnose zika virus is after 30 weeks of pregnancy. A positive zika virus results might be an indication of fetal infection. This information is vital for determining the correct progressive management (Postpartum follow ups, delivery planning, continued ultrasounds).
What is the effect of zika virus on future pregnancy?
Because zika virus has a potential to cause birth defects such as microcephaly, it is important to plan for each pregnancy in the context of zika virus. For a healthier pregnancy, couples should undergo testing prior to pregnancy.
The good news is, there is no evidence that zika virus can cause effects on future pregnancy after the virus had cleared from the body. Women looking forward to conception using anonymous sperm donors should follow proper semen testing guidelines to avoid the risk of being infected during pregnancy.
What percentage of zika-infected pregnant women have babies with birth defects?
Facts state that zika birth defect prevalence is 1 to 13 percent of pregnant women. Research has shown that 28 percent of fetuses from infected mothers have significant problems as compared to those of non-infected mothers.
What stage of pregnancy is most dangerous to be infected with zika?
Detailed facts about Zika virus show that it can harm a fetus at any stage of pregnancy. However other studies have shown that infections during the first months of gestation are more damaging.
“Early stages of pregnancies are associated with fetal developments, probably the reason why the virus seems more dangerous” reports Karen, a certified clinical pediatrics.
Can you assume that babies born without microcephaly are healthy?
No.There are facts of the brain damage by the virus that might not be associated with microcephaly. It will also take years to note the effects of like babies.
Mostly the effects are noted as the baby approaches major milestones such as walking, talking and learning.
If tested positive for zika, can the baby be checked for the infection at birth?
The baby will get checked for the virus immediately after birth. The guidelines state that infants born to mothers with positive zika test should have comprehensive physical examinations including head circumference measurements, hearing screening, and developmental assessments.
- Depending on the length of zika virus exposure, the healthcare provider determines whether further evaluations are needed.
- If so then a head ultrasound is scheduled, together with the ophthalmological assessment. Depending on the results of the evaluations, specimen testing might be considered.
Pathological evaluation involves the use of fetal tissues to make diagnoses. This kind of evaluation is crucial in determining congenital zika syndrome. Additionally, the evaluation is helpful in evaluating women who seek healthcare guidance after 12 weeks of gestation onwards.
Can I breastfeed if I have zika virus?
Unfortunately, it is not advisable to breastfeed when infected with the virus. The virus has been found in breast milk of infected women.
However, there have been no reported cases of children infected with zika through breast milk. Most children who contact zika from mosquitos do not develop severe symptoms as compared to adults.
Different researches claim that the benefits of breastfeeding outweigh any potential risk of zika virus infections through breastfeeding. If you have doubts about breastfeeding your child, be sure to talk to your healthcare provider, you will be advised accordingly.
Do men need to worry about Zika?
Yes. Both men and women can transmit this virus sexually. Men who have been exposed to zika such as by traveling to an affected area should avoid infecting their partners by using condoms during sex until virus completely clears from the blood system
Is there a vaccine from zika?
Unfortunately, Zika virus does not have a vaccine. However its symptoms can be treated and as a result provides relieve. Because there is no cure, the infected person can still pass the infection through sex or body fluids or to a growing fetus during pregnancy.
How can I prevent zika infection during pregnancy?
Since there is no known zika medication and vaccine, the best approach for prevention would be to avoid mosquito bites. Because you might never know when the zika virus might spread to where you live, it is always good to follow the following precautions:
- Apply a mosquito repellant. Be careful about the repellent you purchase, talk to your doctor to suggest one for you, in case you have no idea which one to go for. The recommended type of repellant is one with picaridin, eucalyptus, oil of lemon and active DEET ingredient.(DEET is a standard, all mosquito repellant are tested to see if they meet the DEET criteria).Do not apply mosquito repellant under a sunscreen, apply the repellant unto your feet too, avoid eyes and wounds when spraying the repellant.
- Always wear long sleeves, pants that are permethrin treated; you can buy them treated or simply treat them yourself.
- Stay indoors during peak mosquito hours, especially in the evenings.Aedes mosquitos are also present at night, even though they are less active.
- Sleep in unscreened rooms with closed windows with enough air-conditioning.
- Avoid traveling to zika affected areas, if in any case, you have to, talk to your health care provider about the preventive steps you should take.
- If you are thinking about getting pregnant with donated sperm, ask if you can test the sperm for zika virus. If the sperm is not tested, you will be at a higher risk of contracting the virus.
- If you work in the hospital, laboratories or any health setting, follow the work place safety rules. Always wear gloves, masks, and goggles when needed to. Do not handle body fluids or any lab samples with your bare hands
- Remove or drain water near your home or work place. Stagnant water creates a perfect environment for mosquito breeding. Additionally, to minimize the spread of the virus it is recommended that you cut long grass and bushes around houses, these are areas where mosquitoes hide and live.
- Always make sure that your baby’s stroller is covered with a net. Put a mosquito net across the baby stroller making sure that it doesn’t touch the baby’s face.
- Exercise indoors because mosquitoes are attracted to carbon dioxide and sweat. Your body produces both of these but increases during exercises.
- Treat your clothes with permethrin, a chemical used as an insecticide. The permethrin treatment offers protection through 60 washes. n
Remember
It is important to note that just because a pregnant woman tests positive for zika virus, the facts remain that it does not automatically mean her baby will have defects.
SOURCES AND REFERENCES
- Zika virus (August 2018): https://www.cdc.gov/zika/about/overview.html
- Zika viruses, self-management (Jan 2016): http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/zika-virus/manage/ptc-20189439
- Zika virus (May 2013): http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/zika-virus/Pages/Introduction.aspx#GBS
- 4What you need to know about the zika outbreak (May 2016): https://health.clevelandclinic.org/2016/01/cdc-issues-travel-warning-due-to-zika-virus-outbreak/
- Prevention: Zika virus (May 2014): https://www.cdc.gov/zika/prevention/index.html
