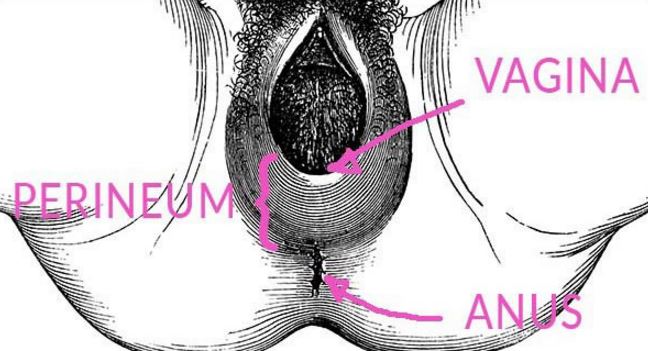
During childbirth, many physical changes can happen to your body. Vaginal cuts and tears are common especially if the process is tedious.
Tearing your perineal muscles is one of the possible risk factors of a natural delivery.
Other possible causes are wiping hard and infections that cause a severely itchy groin area. Here’s a detailed guide to the causes and how to heal perineum cuts.
Whether it is a minor or a major tear, the perineum is a delicate area. Even tiny tears can cause swelling, itching and burning sensations during urination.
Larger tears can cause a lot of discomforts, and even after stitches, one can still feel sore and uncomfortable.
- Treatment of the tears depends on the degree (1st degree, 2nd degree or 3rd degree).
- Major causes of perineum tearing in females include childbirth and infections.
- However, there are other factors that highly contribute to such cuts such as bowel movements.
- Severe cuts can happen naturally but are very uncommon, occurring only in less than 3 percent of all births.
What is a perineum tear?
It is spontaneous laceration of the skin and other tissue structures which, in women, separate the vagina from the anus. Who is at risk of such cuts and lacerations?

Most women giving birth during their adolescence and those of high birth weight have high chances of tearing their perineal muscles.
- Tears vary widely in severity, the majority are superficial and require no treatment. Severe ones can cause bleeding, chronic pain and/or dysfunction.
First, second and 3rd-degree tears
Here, laceration is usually limited to the fourchette and superficial perineal skin or vaginal mucosa. But in the second-degree tear, the laceration extends beyond fourchette, perineal skin and vaginal mucosa to the perineal muscles and the surrounding but not the anus.
However one of the most severe tears is the third-degree tears whereby the fourchette, perineal skin, vaginal mucosa, muscles, and the anal sphincter are torn.
Fourth-degree tear
In the 4th, the fourchette, perineal skin, vaginal mucosa, muscles, anal sphincter and the rectal mucosa are torn.
An episiotomy is commonly confused with a tear. It is a cut made by a midwife or doctor during childbirth to facilitate passage of the baby’s head.
Causes of perineum tears in females?
There are different factors that lead to cuts and injuries around this area. Here are the common causes in females:
1. Torn perineum from wiping
The perineum area is delicate. Extra care should be taken during wiping. Unnecessarily excessive or hard wiping will cause trauma.
You are advised to wipe the area from front to back with soft tissue paper to avoid a tear from wiping the wrong way.
Also, drop used toilet paper and pads into the toilet after each wipe to avoid perennial area contamination and likely infection.
2. Childbirth
The head of the fetus is large in comparison to the birth canal. As the head passes through the pelvis, the soft tissues are stretched and compressed. The risk of a severe tear is largely increased when the baby’s head is lying to the posterior.

Again, a tear is likely to occur when a woman gives birth for the first time. This is because during this time the perineum tends to be tight, hence will be subjected to trauma. Serious tears occur when:
- You have been pushing for long in labor
- Your baby is very large(More than 4kgs/8.5 albs)
- Your baby is face-up in the posterior position
- Forceps or other devices are used to assist the birth of your child
- You give birth lying on the bed. The best position to birth is on` all fours’ this way the baby exerts less pressure on the perineal muscles.
- The second stage of labor lasts more than one hour.
When minor tears occur, your doctor is likely to prescribe you some antibiotics and pain relievers. If the perineum tear is very large, you may need stitches. The stitches are likely to stay in for about two weeks, and at the end of this period, your tear will have healed.
3. Sexual intercourse
There are times, due to various factors that the vagina doesn’t lubricate itself well. In this event, the penis is unable to penetrate easily, and a tear occurs as a result. Other causes of a tear during sexual intercourse include:
- Various positions that put undue stress on the lining of the vagina.
- An abnormally large or small vagina can lead to tearing during sexual intercourse.
- Vigorous sexual intercourse can lead to tearing especially when the thrusting is too intense.
- Also, a tear can occur when a woman uses sex toys that are excessively larger than her vagina. Notably, some women have a thin lining that can be torn more easily than normal, which leads to tearing even with gentle intercourse.
Here is how to reduce chances of tearing during sex:
- Always make sure you are properly lubricated to allow easy penetration. You can try and use commercial hypoallergenic lubricants for the same purpose.
- Always looking forward to more vaginal stimulation by your partner to help reduce the worry of a possible perineum tear during sex. You can communicate with your partner about using different techniques to have you achieve the mood.
- Experiment with positions that are less likely to lead to a tear. The woman on top position, in this case, will give you the power to control the sexual activity and avoid a tear.
4. Yeast infections
Before the perineum tears, if there is a yeast infection, you will notice swelling and irritations. Sometimes the tear comes as a result of continuous itchiness and scratching.
Some yeast infection discharges can be very itchy, causing endless discomfort. The more you scratch, the bigger the chances you will tear your perineal wall.
The infection further spreads causing blisters that eventually burst causing you more pain around the perineal area.
5. Bowel movements
Anal fissures or tears occur during constipation. The cracks or tears occur in the tissues aligning the anus from the inside. The area is brought into line with several nerve endings, explaining why this is the most painful kind of tear you can experience.
- If such tears are not adequately managed by visiting your doctor, then chronic pain and even hemorrhoids might occur. During an anal tear, the internal muscles get into spas which may additionally get painful.
It is advisable that you drink a lot of water to soften your stools, also try and eat natural foods with fibers to help you move your bowel easily.
Symptoms
The torn skin around the vaginal area can cause discomfort. Given the crotch can be sweaty, irritation can arise from perspiration. Here are some of the most common symptoms of a perineum cut.
Itching and pain
The perineum is surrounded by several nerve endings. In the event of an injury or trauma to its tissues, pain and itching are inevitable. The pain is especially intense when passing urine or stool.
Itchiness can also arise from scarring tissue as the tear tries to heal. Salty sweat can also cause irritation, leading to the feeling of itchiness.
Incontinence
An injury to the external or internal sphincter or even the surrounding nerves might lead to severe injury to the urinary system. More serious fourth-degree sphincter tears convey a greater risk of fecal incontinence than the smaller third and second-degree tears.
- Fecal incontinence is known to be more common with women who deliver per vagina and have visible vaginal tears. Diarrhea is the first sign of fecal impaction in most cases.
There is an increased urgency in both fecal and urinary incontinence incidences. The injury to the nerve endings simply interferes with the sensory perception of the muscles. Other symptoms include:
- Pain during and after sex
- Pain or much relief after bowel movements
Treatment
How long does a vaginal cut take to heal? Healing time depends on the severity of the tear and the treatment administered.
Treating the cut involves a lot of examinations to rule out possible complications. Here is what to expect during the doctor’s appointment:
- Blood and urine tests will be done. If you have an abnormal discharge, a sample of it will be sent to the laboratory for culture and sensitivity and also other pathological studies.
- In case you have an infection and at the same time, stitches on the perineum, they might be removed so that the infection can drain.
- If you have blood collection on the perineum, it will be drained off.
- A rectal examination might also be carried out to rule out hemorrhoids and blood clots.
How to heal a torn perineum depends on the results of the doctor’s examinations and tests. Your doctor will deduce the best treatment for your case.
A tear that is longer than 2 cm or about an inch will need repair. Nevertheless, you might get antibiotics depending on whether you have an infection or not. Some infections might heal on their own.
Naturally, your doctor might just administer painkillers and give you a follow-up date for medical evaluations. Some minor infections do not need an antibiotic intake.
Home treatment options
Here is how to heal a torn perineum using home remedies:
- Take a stool softener
This will reduce your need to strain when you have a bowel movement. Do not resist a bowel movement when there is an urge to, as it will lead to constipation.
Also eating foods rich in fibers will help make your stool soft and easy to pass.
2. Stay clean and dry
A moist torn perineum will only lead to infections. Dry the area gently with a soft, clean towel after a bath or warm water soak. By doing this, you will shorten healing time.
3. Rest
Avoid strenuous exercises and unnecessary movements. Give yourself ample time to heal. You are likely to be barred from heavy activities for at least two weeks. Stay off your feet as much as possible until treatment is effective and healing takes place.
4. Avoid practices that can worsen your symptoms
Avoid salt baths, powders and perfumed lotions on the perineum. Avoid squatting to keep off from stretching the skin too much. Also, do not engage in sexual activity until healing is complete.
Additionally:
- Use ice packs made of clean gauze soaked in a cold witch hazel to relieve pain
- Sit on doughnut pillow to avoid putting pressure on the area.
- Avoid standing and sitting positions that put pressure on this area, also avoid standing or sitting for longer periods of time.
- Lie on your side when resting or napping
Can you prevent it?
Even though some vaginal tears are unavoidable, there are precautions you can take to help prevent some from occurring. Here are the prevention tips:
- Practice Kegel exercises ahead of delivery to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
- Take your prenatal vitamins and eat balanced diet to help your muscles build strength ahead of childbirth
- Use a lubricant during sex and when it is time to push in delivery
- Keep the perineum warm to increase blood flow and soften the muscles (Get a warm towel and press on the muscles to accomplish this)
- Treat yeast infections on time, always visit your doctor for reviews when the infections don’t seem to cure.
- Avoid using sex toys too large for your vagina.
When to see a doctor
In some events treatment for the perineal tear may seem ineffective, it is advised that you visit your doctor when:
- There is increased pain at the incision site
- Increased fever
- Significant swelling
- Foul smelling discharge from the vagina
- Intense pain during urination
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen, vagina together with the perineal area.
- Increased vaginal bleeding
- Passing gas or stool from the vagina
SOURCES AND REFERENCES
- Episiotomy (June 2016): http://www.mayoclinic.org/episiotomy/IMG-20006450
- Lacerations (May 2013): http://www.med.umich.edu/1libr/HealthyHealing/Laceration-ForthDegree.pdf