After ovulating, your vaginal secretions can look creamy, egg whitish, thick or even yellow. But what does it mean? What does it look like if pregnant and when should you see a doctor?
Ovulation is one of the major stages in your menstrual cycle in which there are observable signs. You are likely to feel some cramps, see a little discharge among other signs.

What happens during ovulation?
During ovulation, a follicle will burst to release a mature egg into the ovarian cavity. The egg will then start travelling in the fallopian tube towards the uterus.
- If fertilization occurs, it will take place in the fallopian tubes.
- The egg will attach itself to the uterine wall.
- If fertilization does not take place, the egg will be washed out of the body during menstruation.
- The color, texture and amount of cervical mucus after ovulation may vary depending on what occurred.
The ovulation process is under the influence of hormones just like all other reproductive processes. In the first phase of ovulation (called the follicular phase), hormones cause the maturation of the egg in the follicles.
This phase lasts from the time you had your period to the midway of your period.
In the second phase which is the ovulation phase, an increase in the estrogen hormone leads to a rise in the luteinizing hormone (LH) and the follicle stimulating hormone (FSH).
This rise occurs for about 24 to 36 hours (a day to a day and a half). Each of the hormones released has their own purposes.
- The luteinizing hormone is the one which ruptures the follicles to release the mature egg into the ovarian cavity.
- The follicle stimulating hormone, on its part, is responsible for the growth and maturation of the follicles and the eggs they have inside them.
- Together, these hormones oversee the ovulation process.
Ovulation will occur midway of the menstrual cycle. For a regular period of 28 days, you can expect ovulation and its signs to appear any time around the 14th day. It may come earlier or later than this date since bodily processes are rarely accurately estimated.
Monitoring cervical mucus before and after ovulation (DPO) can help you determine when your ovulation will occur. You will be able to know when exactly you are fertile and ready to conceive (get pregnant).
During ovulation vs. 1 day after
What does CM look like during ovulation vs. a day post ovulation (1 DPO)?
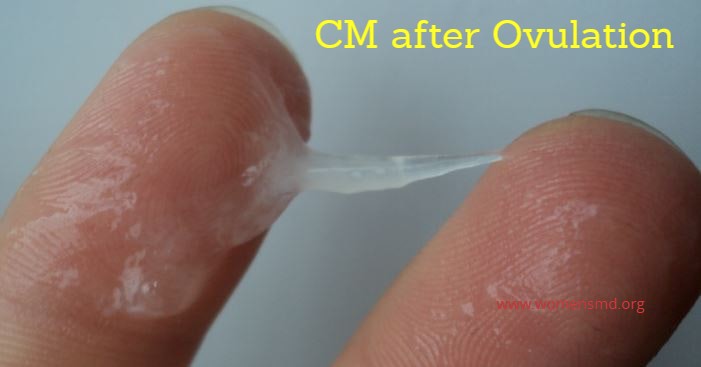
You will notice that vaginal or cervical mucus during ovulation will be stretchy and have an egg white consistency.

The egg white mucus here can be compared to a raw egg. This type of mucus is the best for sperm to swim and survive inside the body until they can fertilize the egg.
After the ovulation process is over, the mucus will change back to the normal clear to slightly white color. However, the discharge from the ovulation process will dry up and become sticky.
After the drying up of the mucus and reverting to the normal discharge, you may notice an increase in the mucus with the egg white discharge appearing once more.
This will likely occur about a week after ovulation. It would be a sign of implantation – is the attachment of the fertilized egg onto the walls of the uterus (if fertilization occurred).
In summary, here are the differences in cervical mucus during ovulation vs. cervical mucus a day after ovulation.
| CM during ovulation | CM a day or more after ovulation |
| Stretchy, egg white vaginal mucus. It is more likely to be clear in color. | Dry, slightly thick from a day post ovulation is over. It can be creamy yellow or pearl whitish in color. |
| Wet and slippery mucus, meaning you are fertile and ready to conceive. | Dry and creamy to signify the end of your fertile period. |
Another aspect of importance is that, when carrying out a self-examination of the cervical mucus, you should be careful not to take a wrong reading due some conditions.

In some cases, the situation might give you a wrong sign. Be careful of the following:
- Avoid checking for the CM during or a short while after sex. This is because the mucus you will find will be heavily influenced by sex hormones.
When you are sexually aroused, the case is the same as you will have a specific type of cervical mucus different from the rest of the mucus.
Even after two days from the day you had sex, you may still have semen inside the vagina which can be confused for the egg white discharge.
- It may also be difficult to know when exactly you are fertile from the egg white discharge when you have the polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). This is because this condition is known to cause an egg white discharge randomly.
- Even when you are ovulating, you may not see the natural types of mucus when you are using some drugs such as Clomid and antihistamines.
- At times, you may never see mucus which has an egg white color and consistency. If this occurs and you go for several menstrual cycles without this particular type of discharge, you need to talk to your doctor. It could be a case of hostile cervical mucus which is a major cause of infertility.
- There are cases where you might have the egg white discharge right before your period hence the need to correctly track the menstrual cycle to know when you will be fertile.
If you factor in all these aspects, your test will be accurate.
What does CM look like after ovulation?
After the ovulation process, the cervical mucus will change its color from the egg white to a slightly white and dry for a few days.
Afterwards, it will retain its color but the dried mucus will be washed away and replaced with a fluid in small amounts.
There is a misconception that egg white is white in color. On the contrary, egg white is mildly yellow and mostly clear in color. It only becomes white when the egg is cooked. The consistency of the egg white is what makes it very similar to the cervical mucus seen during ovulation.
If pregnant
What are the changes in CM after conception? When you get pregnant, the egg released by the ovary would meet with a sperm and together they will form an embryo.
You can easily notice the pregnancy if you are keen with the color and consistency of the cervical mucus after ovulation. Given that the pregnancy will occur after a week from ovulation – during implantation -, you should notice the change in the cervical mucus after that time.
CM after ovulation if pregnant will become thick and milky white in color and in higher amounts. It is referred to as leukorrhea and an early sign of a pregnancy.

It will be easy to know if it is a pregnancy or not if you take note of the other signs of pregnancy which include:
- Swollen and tender breasts
- Slight cramps
- Diarrhea and stomach gas
- Fatigue
- Food cravings and aversions
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation
- Headaches
- Mood swings
You can take a pregnancy test on the day you were expecting your next period.
Be careful to draw a line between a thick white mucus and a cheese-like white mucus. The two types of mucus share many traits but they represent different things. The thick white mucus is a sign of a pregnancy while the cheese-like white discharge is a sign of a yeast infection.
If NOT pregnant
If you do not get pregnant after the ovulation, your cervical fluid will undergo changes
The changes include drying up to form white dry mucus followed by reverting to the normal clear to slightly white mucus.
What do the colors mean?
The changes you notice in your vaginal mucus before, during and after ovulation in terms of the texture and color carry different meanings as follows:
Creamy
The creamy cervical mucus you will see is a sign of an incoming ovulation. It is a bit sticky but not a lot. This type of fluid is not good for the fertilization process as they provide poor conditions for the survival and movement of sperms.
Even after ovulation, the creamy secretion will largely prevent getting pregnant. If you intend to get pregnant, don’t get your hopes high when you see this type of vaginal mucus.
Thick and sticky
The thick and sticky cervical mucus means you are not yet ovulating. In this case, if you plan to get pregnant, it would not be a good time for it.
The consistency of this CM makes it difficult for the sperms to move and survive inside the body. While you may still get pregnant when seeing this type of mucus, chances are low.
Egg white CM post-ovulation
The egg white cervical mucus is a sign of ovulation.
Its consistency allows the sperms to survive and easily move towards the ovaries for fertilization. If you intend to get pregnant, this mucus indicates the right time to try to conceive.
Yellow in color
The yellow cervical mucus is referred to as leukorrhea. It is a normal part of the body although its amount goes up during a pregnancy. When you see leukorrhea, you are likely pregnant.
Leukorrhea will be present all through your pregnancy. It is a mix of the normal bodily fluids and dead cells and thus has a cleaning role. It also has a mild odor to it which is normal.
The yellow CM should, however, not be accompanied by any symptoms of a disease such as;
- Pain
- Itching
- Nausea
- A strong odor
- Abnormally large amounts of the discharge (excessive vaginal discharge)
Other post ovulation signs
Besides the types of cervical mucus post ovulation described above, the other signs that you have ovulated include:
- Changes in the basal body temperature with a rise being noted during or after ovulation. The basal body temperature may drop for a while just before ovulation but then rises sharply when ovulation sets in.
- When you insert your finger into the vagina during ovulation, you will notice that the cervix will be wet, open, high and soft compared to normal times.
- A heightened sense of smell, vision and taste.
- A higher than normal sex drive.
- Abdominal bloating.
- Breast tenderness
- Light cramps
- Light spotting.
You may see only a few of these signs or none at all. In either case, it is perfectly normal. When the spotting and cramps become too much, see your doctor.
How to check your CM
CM changes with each stage in the menstrual cycle and the body at large. To check your vaginal mucus:
- Wash your and dry them up.
- Find a position which allows you to reach the vagina with ease. You can either stand up with legs apart, squat, sit on the toilet seat, or on a comfortable chair on the edge.
- Slowly insert your middle or index finger into the vagina up to the point the knuckles touch the lips of the vagina. Make sure to do so careful not to scratch the delicate inside of your vagina and cervix.
- Remove your finger and take note of its color. Also, press two fingers together and pull them apart.
References
- Cervical Mucus and Your Fertility – American Pregnancy Association
- Vaginal Discharge Early Signs And Symptoms Of Pregnancy – BabyMed.com
- Vaginal Discharge During Pregnancy – American Pregnancy Association